With heavy usage over a longer period of time, banknotes eventually become unfit for use. These notes are then returned to cash centres across the world. Once there, reliable banknote destruction systems are used to securely and sustainably dispose of the notes. This destruction process is typically done in one of two ways: Online or Offline. In this article we explore the differences between the two techniques.
Banknote destruction
Banknote destruction is primarily done by means of shredding and/or granulating the banknotes. The primary purpose of this is to eliminate the chance of reconstitution of a whole or part of a note, and simultaneously reduce the volume and environmental footprint for disposal.
Offline and online banknote destruction defined
1) Offline banknote destruction systems:
These are disintegration systems used by Central Banks for the destruction of bundles ranging from 500 to 10.000 notes and are referred to as off-line disintegration.
2) On-line banknote destruction systems
Central Banks also process banknotes on a single note basis, by means of banknote processing system (sorters). These sorters can be equipped with an integrated shredding module which destroys the genuine but unfit banknotes one by one, this is referred to as “on-line shredding”.
The difference between online and offline banknote destruction
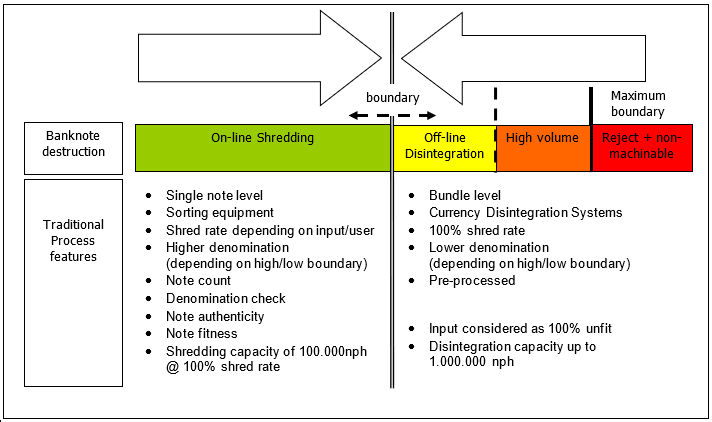
As where off-line disintegration systems are designed for 100% destruction (shred rate) up to 1 million+ notes per hour, the primary goal of the online system or sorter is different. The sorter primarily focusses on processing banknotes while allowing the option to also destroy a part of the total volume of notes that they recognize as unfit during the process. Because of this, sorters have a significantly lower destruction capacity of approx. 100.000 notes per hour when set to 100% shred rate.
The above establishes a certain balance between the off-line and on-line disintegration. The boundary depends on local situation, policies and banknote quality and therefore differ for each Central Bank and even per denomination (see figure 1.2).
 1.1 An off-line banknote destruction system
1.1 An off-line banknote destruction system
Security as the main focus of both methods
As for the entire lifecycle of a banknote, security is the main concern for the user. It is therefore of crucial importance that the destruction of a banknote is done under, at least, the same high security guidelines.
For the safe destruction of banknotes, the following four points should be considered:
- Destruction within a closed environment
- 100% guarantee that all banknotes have been destroyed by the system
- After the banknotes enter the destruction system, touching of the banknotes should be avoided, in order to stay clear of any possible fraud.
- Prevent crossing the input flow of banknotes with the output flow of the waste material or to be in the same area.
1.2 off-line VS On-line banknote destruction
Authentication versus volume and rejects
The Central Bank’s need for authentication may move the boundary to the right resulting in an increase of on-line shredding compared to off-line disintegration (yellow area). Current developments within the off-line disintegration technology may have an opposing driver in favor of off-line disintegration.
When high volumes of unfit notes are to be destroyed the capacity of the destruction process will become an increasing factor to be considered (orange area), investing multiple sorters versus a dedicated off-line disintegration system. This doesn't mean that the two methods can never be combined however. Various sorters can be linked to an off-line system to achieve synergy of the two techniques.
Finally, there will always be a share of banknotes, rejects and non-machinables, that cannot be processed and thus cannot be on-line shredded (red area).
Are you looking for a solution to facilitate large scale banknote destruction? Or are you interested in learning more about different applications for the technique?
The following weeks we will regularly be posting insights on unfit currency management. If you wish to stay up to date with the latest posts, you can do so by subscribing to our blog.