
Towards the end of 2023, Royal Dutch Kusters Engineering carried out an extensive survey involving Central Banks globally in partnership with Reconnaissance International.
This follow-up study builds upon our 2022 research, focusing on the disposal methods for unfit banknotes once they have been withdrawn from circulation and need to be destroyed. The pressing question remains: how are these shredded banknotes handled, considering the variety of disposal methods available? You can read all about the findings of this survey in this blog.
Kind of banknotes in circulation
The shredded banknote recycling process is often arranged depending on the volume of the banknotes, if these are shredded centrally or decentrally, the maturity level of local recycling markets and last but not least important the wide variety of notes in substrates, inks and security features. The re-use of shredded and briquetted banknotes, continues to be done worldwide in various ways. There isn’t an overall policy or solution what to do with these shredded banknotes, each country has a different approach. That also depends on regulations, circumstances, costs and options as well as which type of banknotes there is. For example pure polymer, cotton or composite banknotes or a mix of these. 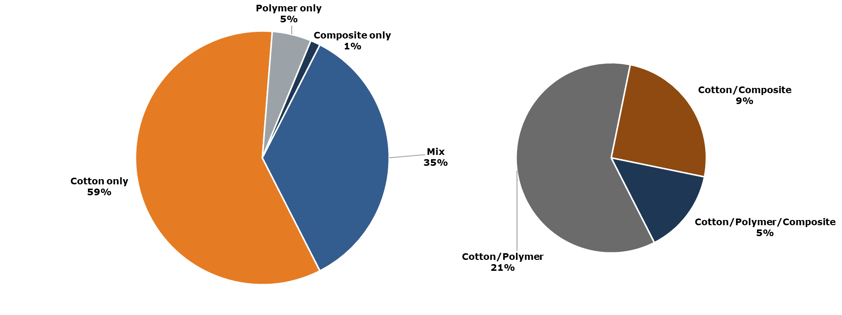
A total of 83 countries from across 6 continents participated in the survey. As shown in the pie chart below, the majority of Central Banks primarily have cotton banknotes in circulation, with a small percentage using only polymer or composite notes. In cases where there is a mix of substrates, the majority consists of a combination of cotton and polymer. The consistent trend observed in the data from the 2023 survey aligns with the previous year's findings, showcasing a steady distribution of banknote substrates among Central Banks globally. This stability implies a certain level of standardization in the types of banknotes in circulation, which could have significant implications for the recycling and disposal methods employed by these institutions. The data not only highlights the prevalence of cotton banknotes but also underscores the importance of understanding the diverse range of substrates, inks and security features present in different currencies. This knowledge is crucial in developing effective and sustainable solutions for the disposal of shredded banknotes, ultimately contributing to a more circular economy within the cash cycle.
Out of the participants surveyed, 16% expressed interest in transitioning to a different substrate. Among those considering a change, the majority showed a preference for switching to composite (44%) or polymer (44%).
Most used methods of disposal per substrates
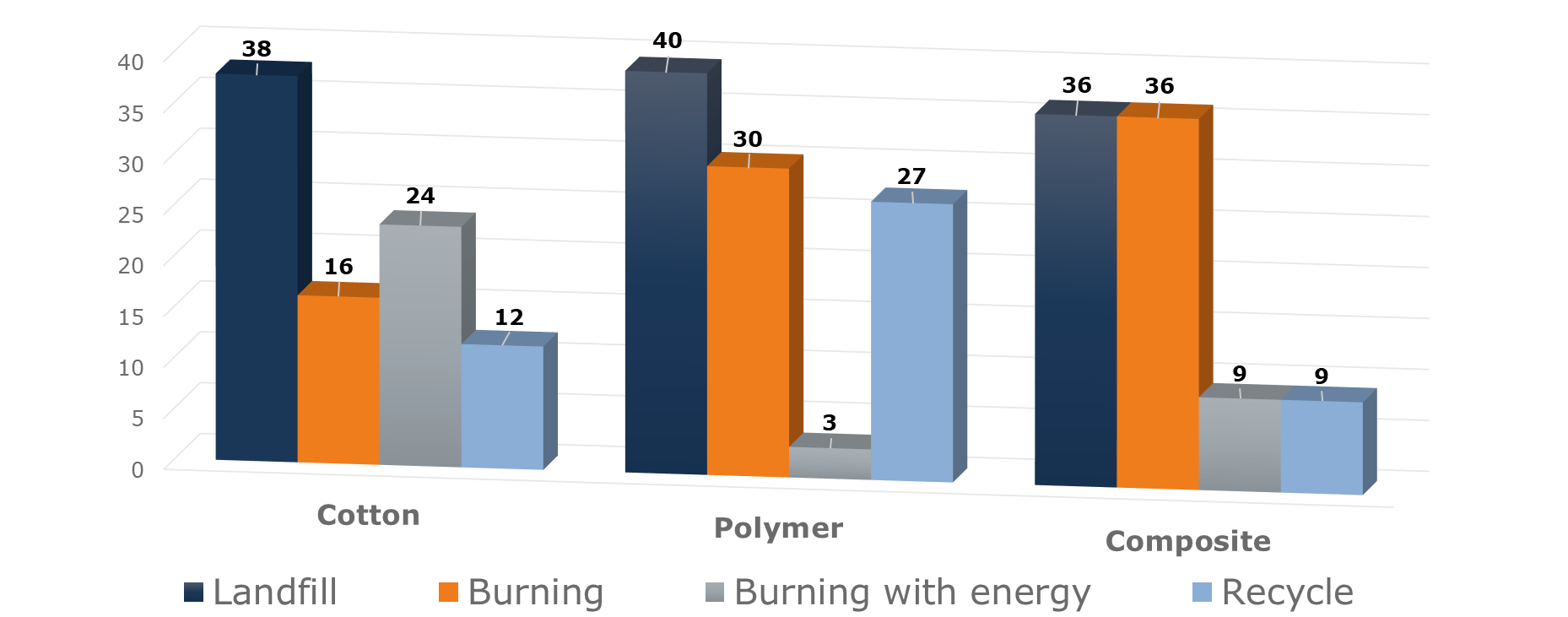
The first chart below showcases the main disposal methods per substrate, with a notable reliance on landfilling and burning by many Central Banks for banknote disposal. Alternative methods such as composting and fuel usage were also considered.
It's crucial to highlight that the survey specifically targeted Central Banks, offering a glimpse into the current practices of these institutions. While some countries have adopted polymer banknotes, the low volume requiring disposal at this stage may hinder the implementation of appropriate disposal methods. For these countries, the volumes were so low that the method of disposal wasn't applicable. These factors were not taken into account in the chart below, which provides a general overview of Central Banks.
Additionally, in the chart below, we examined the number of central banks involved, rather than solely focusing on the quantity of banknotes requiring disposal on an annual basis. Another 10% of cotton disposal also fell into various other categories like fuels and compost.
One of the survey questions also delved into the annual disposal quantities in tonnes per type of substrate. The data we gathered clearly shows that landfill remains the predominant disposal method for cotton, while recycling is the preferred choice for polymer banknotes. It's worth noting that not all substrates are disposed of uniformly worldwide, as not all Central Banks participated in the survey. Nonetheless, this insight offers a valuable overview of current disposal practices.
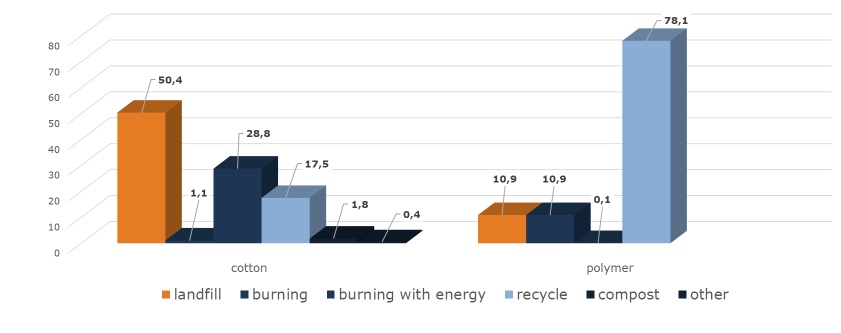
Dumping shredded banknotes in landfills or burning them without energy recovery is not only harmful to the environment but also goes against sustainable practices. These methods continue to be prevalent due to their perceived convenience, the lack of proper infrastructure for alternative disposal methods and the cost-effectiveness they offer in the short term. Central Banks must prioritize sustainable solutions for the disposal of unfit banknotes, considering the long-term impact on the environment and the potential for creating a more circular economy within the cash cycle. By exploring innovative and eco-friendly approaches to handling shredded banknotes, institutions can lead the way toward a more responsible and sustainable future for currency disposal.
The bar charts further in this blog provide a visual representation of how cotton and polymer banknotes are disposed of across different continents. It's encouraging to observe a rising awareness towards sustainability practices in general, with a notable number of Central Banks already embracing methods such as burning with energy recovery, composting and recycling.
Cotton disposal per continent
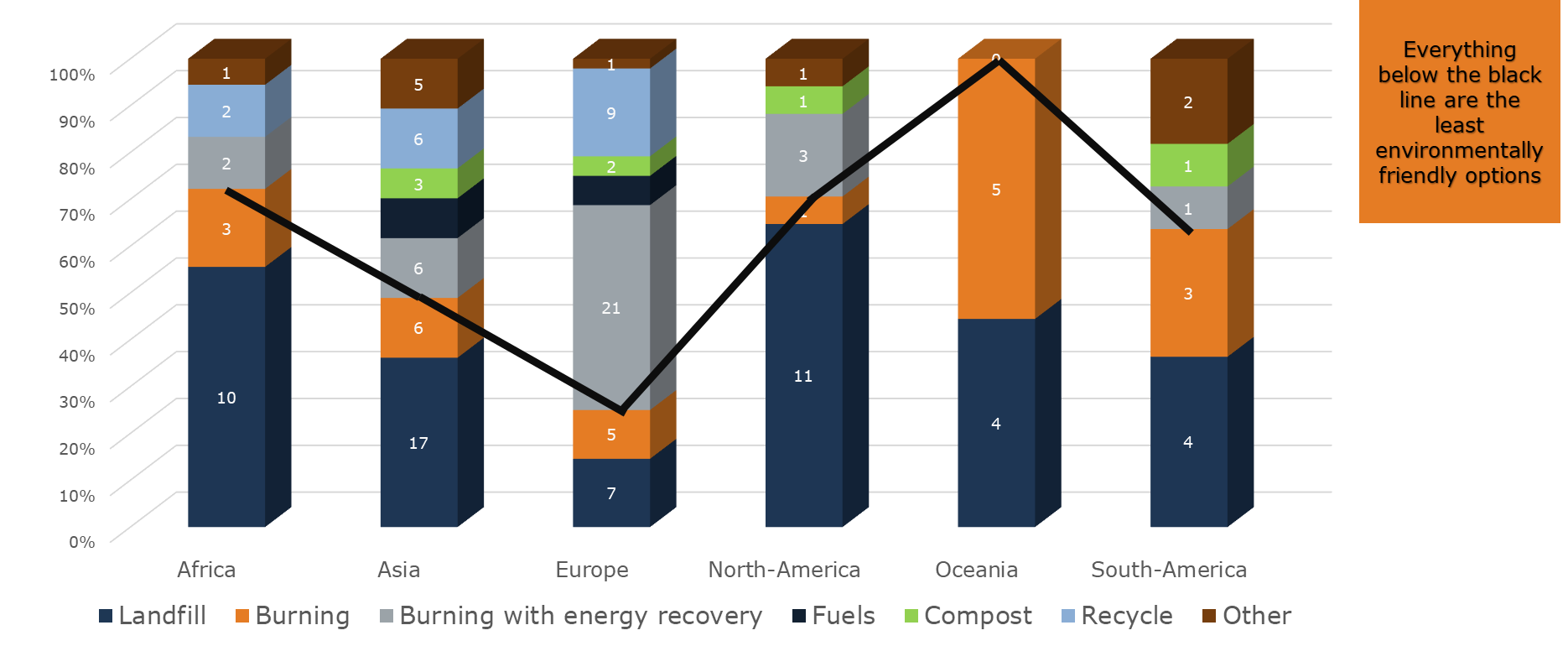
Several continents still opt for landfilling or incineration as their preferred method of disposal. However, there is a growing interest in recycling, with some also exploring innovative alternatives such as using organic waste for fertilization and animal bedding. While certain continents demonstrate a strong dedication to eco-friendly disposal practices like recycling and composting, others display a mix of sustainable and unsustainable approaches. It is crucial to focus efforts on embracing recycling, composting and other sustainable methods to effectively reduce the environmental impact of banknote disposal.
Polymer disposal per continent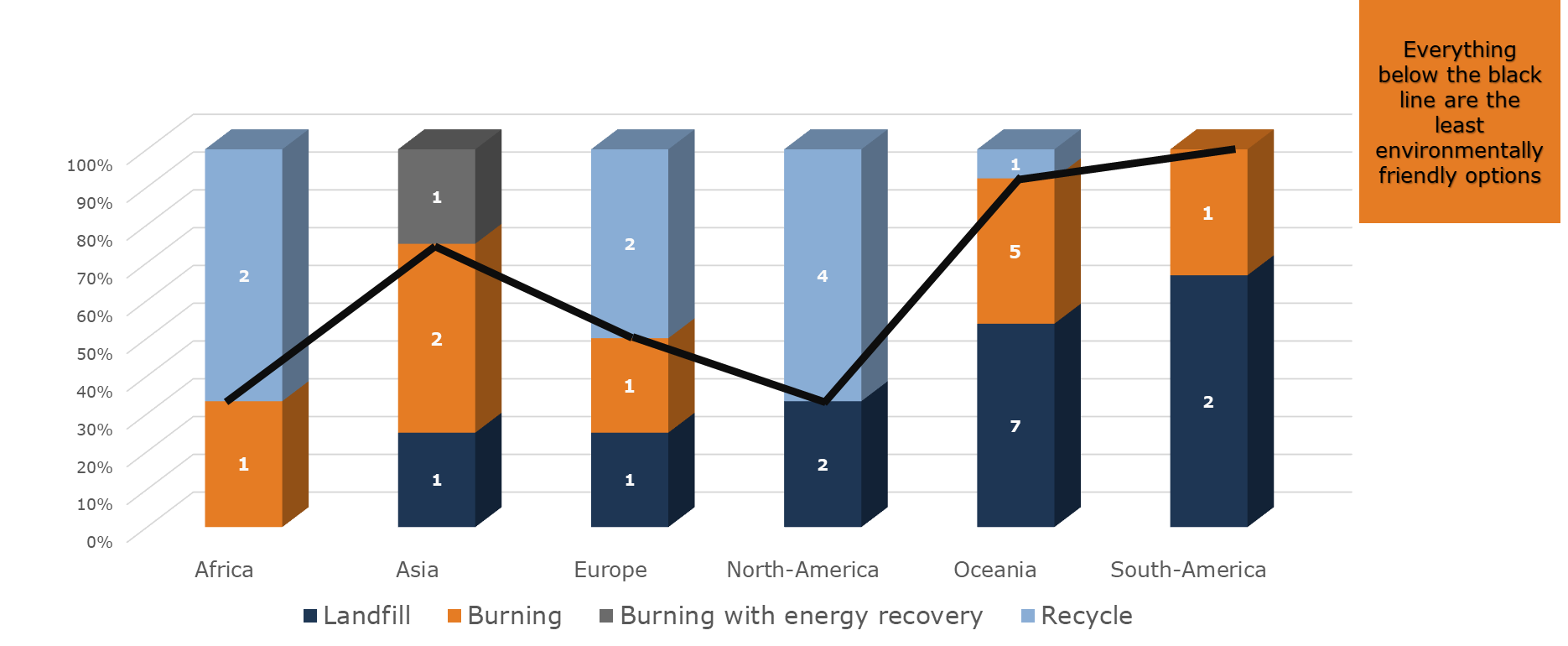
A few continents lead in recycling efforts, while burning remains a prevalent disposal method across continents. Despite some progress in recycling, landfilling and burning still prevail as disposal methods in various regions, emphasizing the need for increased investment and emphasis on sustainable disposal practices like recycling and energy recovery worldwide.
An interesting distinction arises when considering whether a country uses a single substrate or multiple substrates. For instance, among the Central Banks that exclusively used polymer banknotes in this year's survey, 50% are actively engaged in recycling, while another 25% are considering steps towards implementing recycling practices. This indicates a positive move towards sustainable practices in the industry.
Consider to change disposal method
During the 2022 survey, the majority of participants, around two-thirds, indicated no desire to alter their disposal methods. However, 37% expressed a willingness to make a change, with 7% of participants implementing some adjustments in 2023.
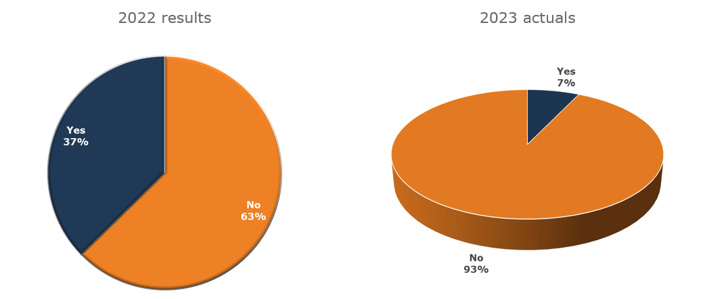
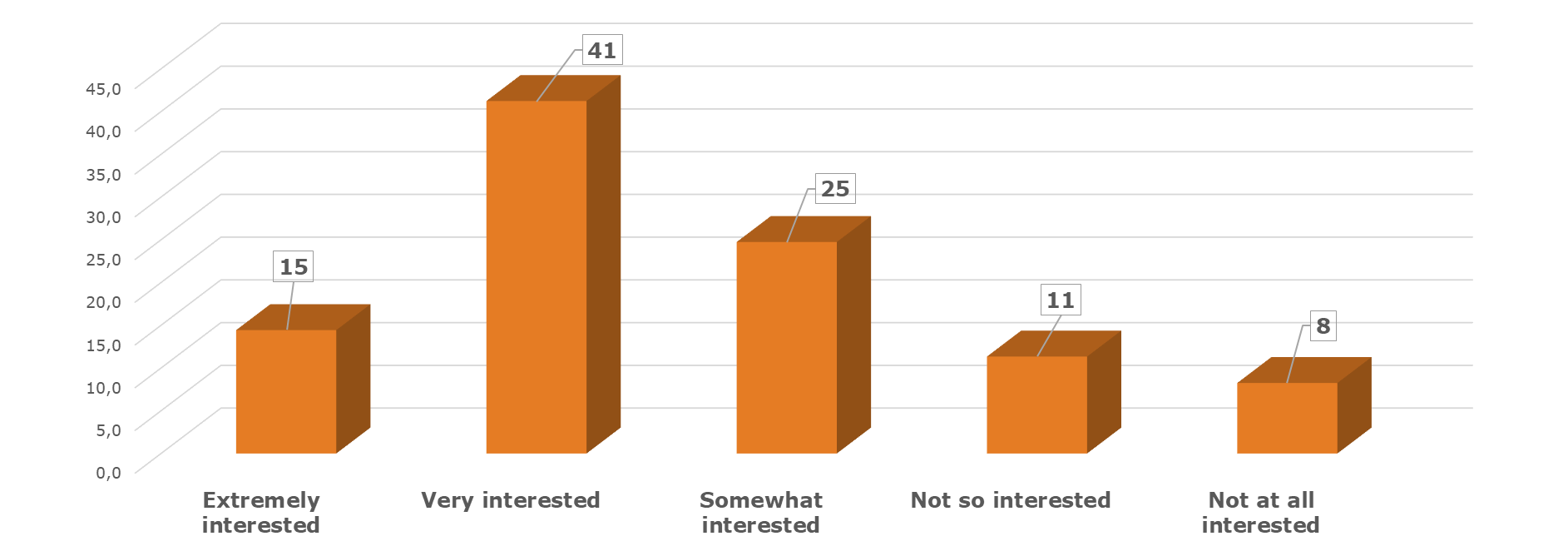
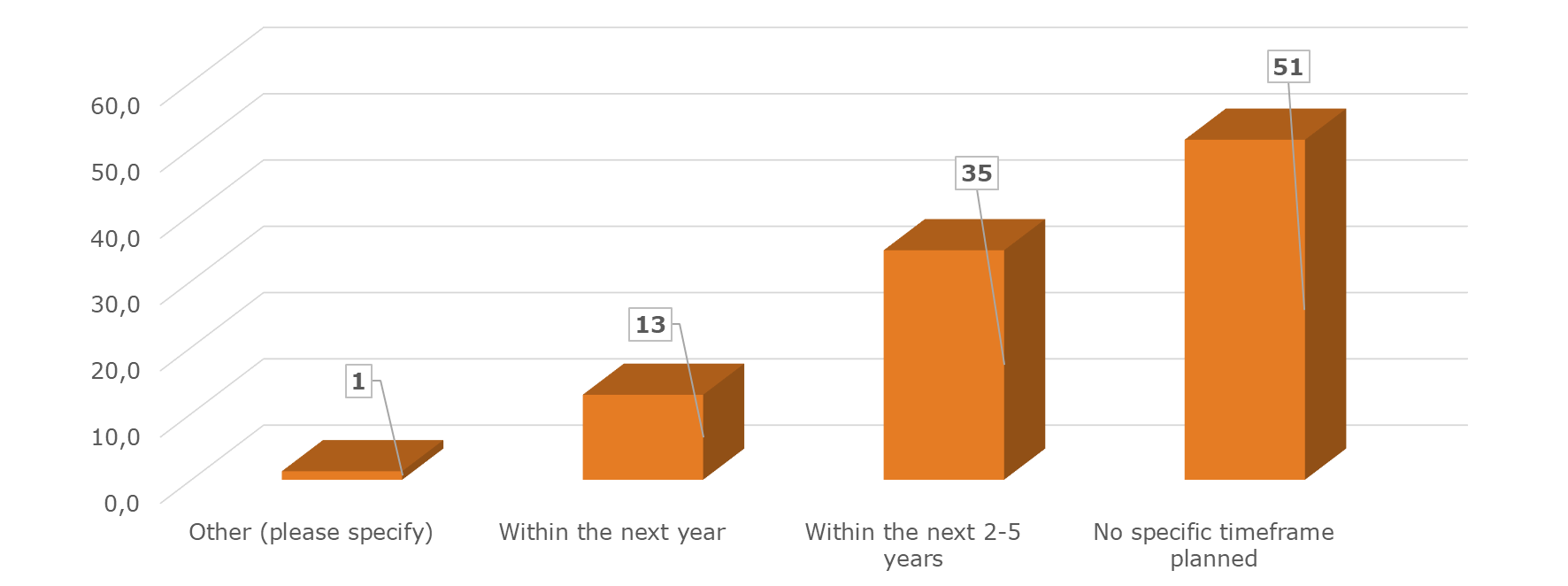
But quite some central banks are interested in moving forward. In the most recent survey, a significant shift is observed, with 55.6% now expressing sure interest in adopting a new approach, and an additional 25% showing some level of curiosity. However, 19% remain resistant to changing their disposal practices. Among those who consider a change, 51% have yet to establish a time frame, while 35% aim to transition to a different disposal method within the next 2-5 years.
Implementing changes in disposal methods is a gradual process that requires careful consideration of factors such as the type of substrate used, available possibilities, the necessity or desire to switch to a different substrate, and the local options for disposal. Despite the time and planning involved, there is a noticeable eagerness to transition towards more sustainable disposal practices. For instance, when a country switches to for example polymer banknotes, it may take years before new disposal methods become necessary. However, this does not imply that they are not making preparations for more sustainable options.
Would you like to get a copy of the Banknote Recycling Study February 2024 summary in PDF format?Simply click the link provided below for more information.
Sustainability
The data in the chart below (presented in percentages) provides a valuable insight into the diverse range of sustainability practices adopted by Central Banks across the globe. While some of them showcase a commendable level of commitment to sustainable practices, others seem to be lagging. This diversity highlights the need for ongoing improvements across different aspects, including transparency, the integration of sustainability into procurement procedures and ensuring a consistent emphasis on sustainability throughout the tender evaluation process.
Addressing these areas for improvement can lead to a more cohesive approach towards sustainability within the banking industry. By fostering a culture of transparency, incorporating sustainability considerations into procurement decisions, and consistently prioritizing sustainability in tender evaluations, Central Banks can further their commitment to environmentally responsible practices. This comprehensive strategy not only positively impacts the environment but also nurtures a sustainable and ethical system for handling the disposal of unfit banknotes, ultimately improving the circular economy within the cash cycle.
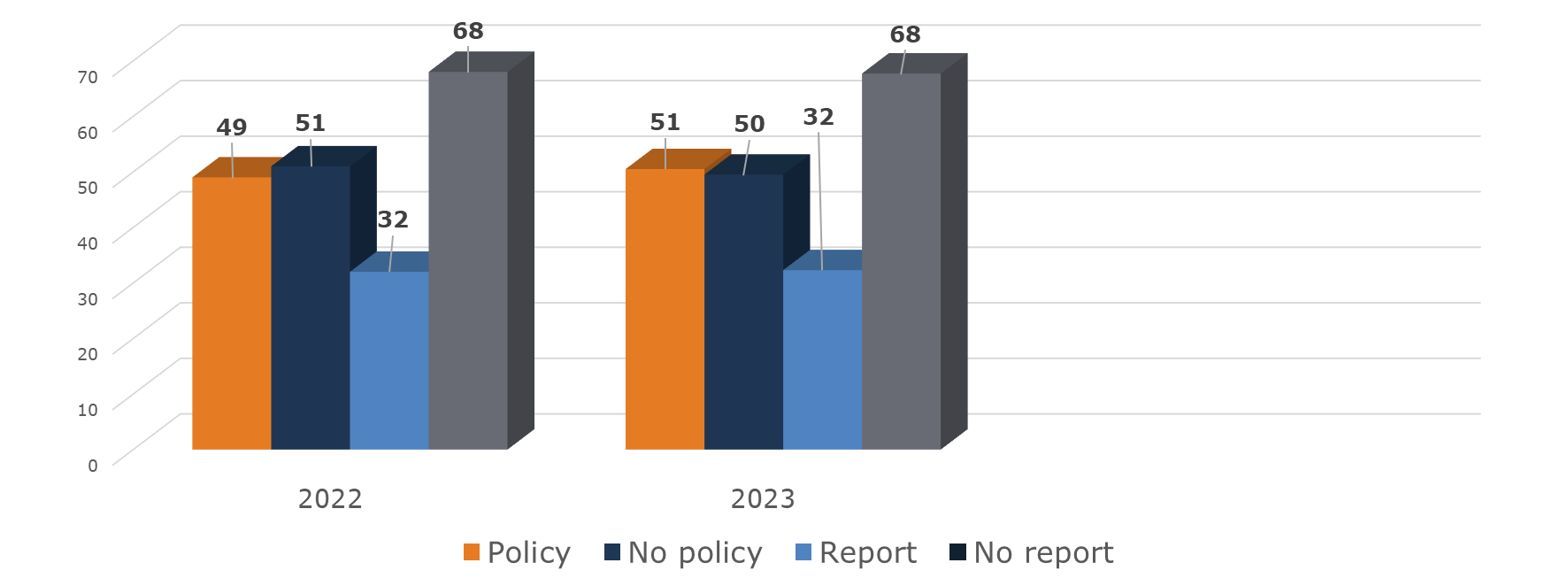
Around half of the surveyed Central Banks have established sustainability policies, showcasing a strong dedication to sustainable practices. Only approximately one-third of entities publish sustainability reports, indicating a need for increased transparency in communicating sustainability initiatives. The level of sustainability integration in procurement processes varies, with a significant portion of organisations seldom or never taking sustainability into account.
The goal of Royal Dutch Kusters Engineering is to unite the industry in fostering a more sustainable cash cycle. By securely destroying and repurposing unfit banknotes, we aim to give them a second chance in a circular economy, thereby prolonging the lifespan of banknotes. Ultimately, we strive to provide comprehensive and enduring solutions crafted from 100% cotton or polymer banknote shreds.
![]()
Recycling solutions for unfit cotton and polymer banknotes
During the prestigious High Security Printing EMEA event held in Sofia, Bulgaria, we had the opportunity to showcase the latest innovative developments in recycling unfit banknotes, both for cotton and polymer shreds. One of the innovative solutions we presented was the transformation of polymer shreds into high-quality furniture, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for repurposing these materials. Additionally, the shredded unfit banknotes were highlighted as a valuable source for producing board panels of exceptional quality, utilizing a mix of 100% recycled material.
These developments not only demonstrate our commitment to sustainable practices but also showcase the potential for creating new, functional products from discarded banknotes. If you're interested in exploring the possibilities of reusing shredded banknotes in a creative and environmentally conscious manner, don't hesitate to reach out to our specialists for a free consultation to discuss the exciting opportunities for repurposing these materials.
3D-Printed furniture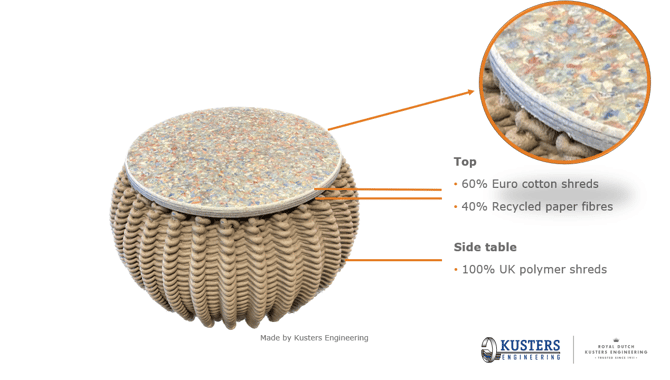
Banknote Industry related products
It can be quite a challenge to effectively dispose of and recycle unfit banknotes, especially with the prevalence of multiple substrates in circulation across many countries today. However, with some slight modifications, these issues can be addressed securely. If you're interested in exploring this subject further, be sure to read our blog for more insights.
If you're curious about how your unfit banknotes could be transformed into innovative new products, don't hesitate to contact us. You'll have the opportunity to explore the possibilities for reusing shredded banknotes sustainably and creatively. We are dedicated to finding unique solutions that not only repurpose these materials but also contribute to a circular economy. Reach out today to start the journey towards a more sustainable future with recycled banknotes.
'In the ideal future, shredded banknotes will seamlessly integrate into a circular economy, promoting sustainability in the cash cycle. Royal Dutch Kusters Engineering aims to unite the industry in secure destruction and reuse, essential for a more sustainable future.'
Jeroen Kusters, Director of Sales
Take part in the upcoming survey
If you represent a Central Bank or Printing Works and are interested in participating in the next Banknote Recycling survey, we value your input. By signing up using the button provided below, you can be part of the upcoming survey outreach. Your insights and feedback play a vital role in shaping the future of sustainable practices within the banking industry. We eagerly anticipate your involvement and cooperation in our ongoing efforts towards a more environmentally responsible and sustainable cash cycle. By participating next time, you will also be entitled to receive a complimentary copy of the report.
Discover our currency destruction solutions
Royal Dutch Kusters Engineering is the world's leading manufacturer of currency destruction equipment. We design, develop, deliver, install and service reliable and secure destruction solutions for all types of banknotes.
If you want to know more about our upgrade solutions to handle polymer banknotes, please download our leaflet: 'From cotton to polymer'.
Keep informed on the latest insights and subscribe to our blog.



